Thermal Bridge Break: What It Is and How to Prevent Heat Loss
🌡️ Thermal bridge break: what is a thermal bridge?
One of the most important aspects when properly resolving construction details in a building is achieving an effective thermal bridge break. This directly affects the thermal performance of the building envelope and indoor comfort.
❄️ What are thermal bridges?
Heat always follows the path of least resistance. For this reason, it flows more easily through materials with high thermal conductivity, such as metals, with aluminum being one of the most common examples.
A thermal bridge occurs when there is a direct high-conductivity path between the exterior and the interior of a building. You can find a more detailed definition on Wikipedia: Thermal bridge.
Cold spots inside building enclosures often coincide with the presence of thermal bridges, with windows being one of the most critical areas of the façade.
🔍 The main problem caused by thermal bridges is that they create areas of the envelope with different thermal resistance. In practical terms, this means that elements such as window frames become points where a significant amount of heat is lost.
💧 In addition, thermal bridges significantly increase the risk of internal condensation. These condensations are especially problematic when they occur within the building envelope, as they are difficult to access and may lead to serious pathologies such as mold growth, dampness, and material degradation.
🧱 Common examples of thermal bridges include: metal grilles and ducts, aluminum window frames, single-glazed windows, solid masonry walls, and concrete or steel lintels.
Not all thermal bridges cause the same level of problems, but windows and ventilation grilles are usually the most critical elements. In this regard, there are specific solutions such as ventilation grilles with thermal bridge break, which help reduce energy losses without compromising ventilation.
🏗️ Whenever possible, thermal bridges should be avoided throughout the entire façade, especially in new buildings. This is not only important to reduce heat losses, but also to prevent condensation problems.
To reduce thermal bridges, construction details must be carefully designed so that frames, lintels, and junctions are resolved with separated sections and low thermal conductivity materials.

🪟 Today, most aluminum windows and frames incorporate thermal bridge breaks. This solution consists of separating the exterior and interior parts of the frame using low thermal conductivity materials such as polyamides or neoprene, which interrupt heat transfer.
In the case of PVC window frames, this issue does not occur, as the material itself has low thermal conductivity.
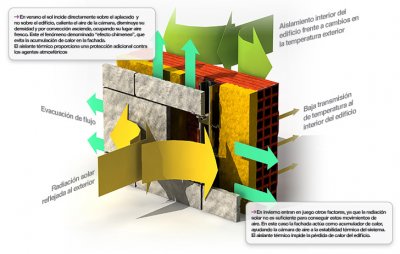
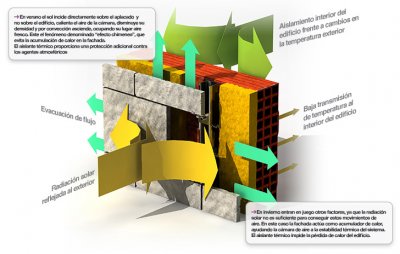
🔗 Another critical area for reducing thermal bridges is the junction between walls and floor slabs. In traditional construction, insulation is often interrupted at the slab edge, creating a thermal bridge at this point.
An effective solution is the use of ventilated façades, where insulation continuity is guaranteed and proper ventilation of the air cavity is ensured.
🏠 In older buildings, improvement options are more limited. In these cases, one of the most effective actions is to replace windows and ensure that, if aluminum frames are used, they include a thermal bridge break.
📋 Summary of thermal bridges in buildings
| Element | Thermal bridge risk | Common solution |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum window frames | High | Frames with thermal bridge break |
| Ventilation grilles | High | Thermally broken ventilation grilles |
| Wall–slab junction | High | Continuous thermal insulation |
| Concrete or steel lintels | Medium–high | Perimeter insulation |
| Uninsulated solid walls | Medium | External or internal thermal insulation |
Content written by the editorial team of construccion.vilssa.


















